Mendel also analyzed the inheritance of traits observed two at a time, that is the seed color and shape. He tried to determine whether two traits would be inherited together or independently of each other.
We already know from Mendel's Law of Segregation that the pair of alleles will separate from each other during gamete formation.
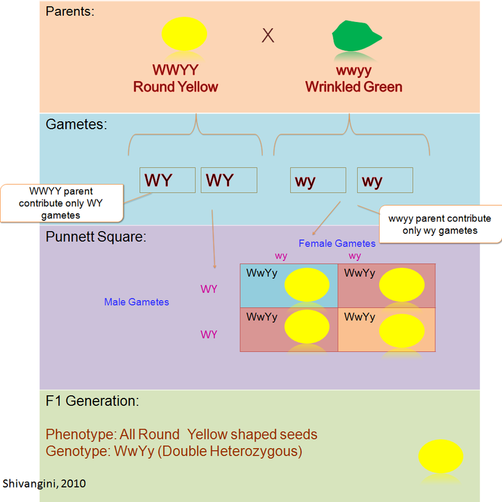
When Mendel cross true-breed Round Yellow, WWYY and Wrinkled Green seed, wwyy, the F1 generation produced Round Yellow Seeds, WwYy. Which is a heterozygous (Figure 3.1).
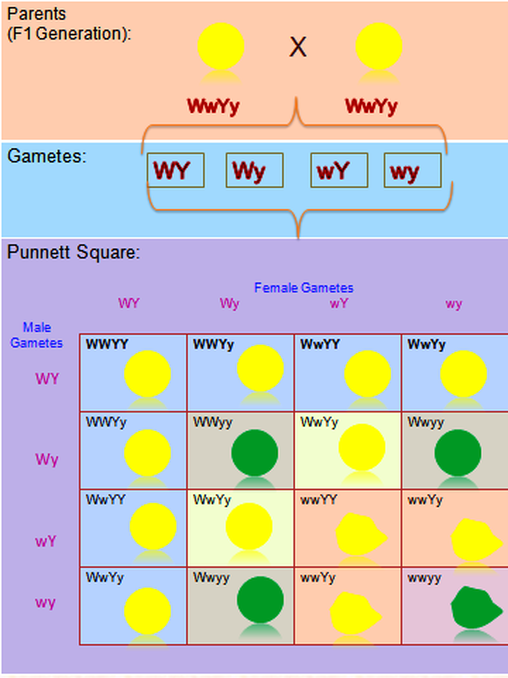
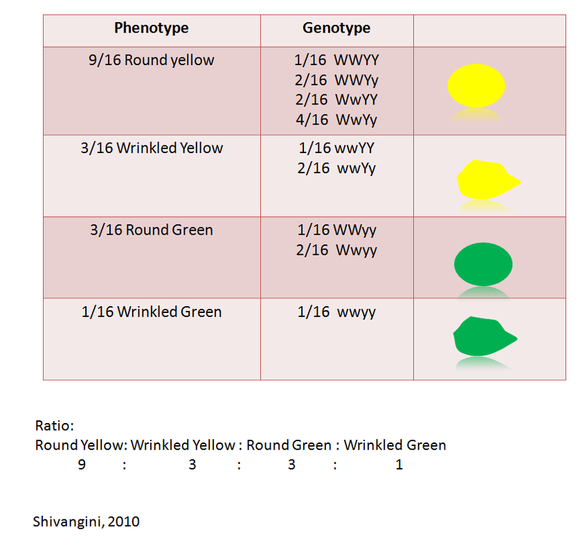
When F1 generation was self-fertilised it produced 9:3:3:1 ratio for Round Yellow seed, Wrinkled Yellow seeds, Round Green Seeds and Wrinkled Green seeds (Figure 4.2).
Phenotype ratio: Round Yellow : Wrinkled Yellow : Round Green : Wrinkled Green
9 : 3 : 3 : 1
Genotype ratio:
9/16 Round Yellow: 1/16 WWYY + 2/16 WWYy + 2/16 WwYY + 4/16 WwYy
3/16 Wrinkled Yellow: 1/16 wwYY + 2/16 wwYy
3/16 Round Green: 1/16 WWy + 2/16 Wwyy
1/16 Wrinkled Green: 1/16 wwyy
From his experiment Mendel reported:
The observed ratio of 315: 108: 101: 1 equals 9.84: 3.38: 3.16: 1. This is close to the ratio of 9: 3: 3: 1.
The ratio 9: 3: 3: 1 suggests that the two characteristics are behaving independent of each other.
To help you understand how we come up with the gametes view the video below . It shows the technique we learnt in school while working with gametes. It is similar to how we expand equation in mathematics.
The video has been made with the use of Slideshare.
Source: http://www.slideshare.net/MuniShivangini/determination-of-gametes-in-mendelian-genetics
Source: http://www.slideshare.net/MuniShivangini/determination-of-gametes-in-mendelian-genetics
Key points:
- Mendel said that yellow seed color was dominant over green seed color.
- The two traits separate independently.
Key concept:
Law of Independent Assortment:
In the formation of gametes, separation of the members of any pair of alleles is independent of the separation of the other pairs of allele, that is, each pair of alleles may combine randomly with either of another pair resulting in the offspring containing all combinations of alleles.
Example : In the mating of Wrinkled green and Round yellow, green will pair with both wrinkled and round randomly and likewise Yellow will pair randomly with Wrinkle and round seed.
In the formation of gametes, separation of the members of any pair of alleles is independent of the separation of the other pairs of allele, that is, each pair of alleles may combine randomly with either of another pair resulting in the offspring containing all combinations of alleles.
Example : In the mating of Wrinkled green and Round yellow, green will pair with both wrinkled and round randomly and likewise Yellow will pair randomly with Wrinkle and round seed.
Click on the video below to understand Law of Independent Assortment better.
Relevance to real life:
Independent Assortment of two traits: Albinism and Deafness follows the same pattern of inheritance as the pea plants.
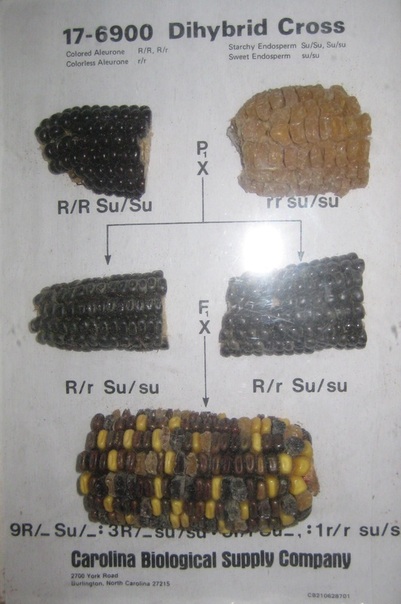
Maize shows independent assortment as well. They have purple and yellow seeds traits and Sugary and non-sugary.
Click here to get a good animated narration about Independent Assortment.
When you open the link and come to the animation part click on to "narrated" if you want to hear or if you want to read click "step through".
When you open the link and come to the animation part click on to "narrated" if you want to hear or if you want to read click "step through".
Now that we have gone through both of Mendel's Laws lets test what we have understood so far.
Click the next page icon to go to the activities section.
Click the next page icon to go to the activities section.